Ginsenoside as a new stabilizer enhances the transfection efficiency and biocompatibility of cationic liposome
Abstract
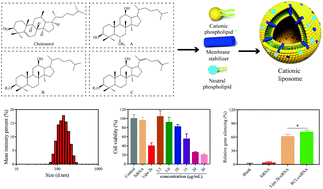
Nucleic acid drugs have emerged as important therapeutics but their clinical application has been greatly limited by their large molecular weight, high polarity, negative charge and short half-life. Cationic liposomes (CLs) have gained wide attention as non-viral vectors for nucleic acid delivery. However, the absolute transfection efficiency of CLs can still be enhanced while their cytotoxicity should be decreased simultaneously. Ginsenosides, obtained from natural plants, possess a similar steroid structure to cholesterol and might be an alternative to cholesterol for acting as a membrane stabilizer of CLs. Herein, seven kinds of ginsenoside-based compounds were utilized to prepare CLs (GCLs) and their efficacy in siRNA delivery was investigated. The particle sizes of the GCLs were 90–300 nm and the siRNA delivery efficiencies were in the range of 23.6%–78.4%. Rg5-based CLs (Rg5-CLs) exhibited the highest transfection efficiency of 81% and the lowest toxicity, with 82% cell viability obtained even at high concentrations. Ginsenosides are shown as promising biomaterials as membrane stabilizers of CLs. Rg5-CLs have been demonstrated as efficient non-viral vectors with high transfection efficiency and good biocompatibility for gene delivery, possessing great potential for gene therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...