Non-contact measurement of internal body temperature using subcutaneously implanted diamond microparticles
Abstract
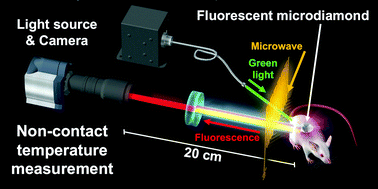
We constructed a highly sensitive fluorescence wide-field imaging system with a microwave source, implanted fluorescent diamond microparticles (“microdiamonds”) subcutaneously into the dorsal skin of a mouse after sacrifice, and demonstrated the feasibility of using optically detected magnetic resonance (ODMR) to measure internal body temperature in a mammal.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...