Biodegradable hyaluronic acid-based, nitric oxide-releasing nanofibers for potential wound healing applications†
Abstract
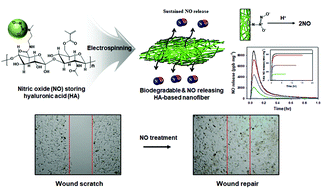
Nitric oxide (NO) is one of the smallest gas molecules with pharmaceutical and potential wound therapeutic effects due to its ability to regulate inflammation and eradicate bacterial infections. Recently, NO-releasing synthetic polymer-based nanofibers have become promising candidates for wound healing due to their facile functionalisation, tunable mechanical properties, and large effective surface areas. However, synthetic polymer-based nanofibers suffer from poor degradability in the physiological milieu, which restricts their use in in vivo applications. In this study, we developed biodegradable and nitric oxide-releasing nanofibers for potential wound healing applications. We synthesised dual-functionalised hyaluronic acid (HA) containing methacrylate groups and N-diazeniumdiolate (NONOate)-NO donor groups and capable of forming crosslinked, electrospun nanofibers, with an effective NO payload, through an electrospinning process and photoinitiated polymerisation. Nuclear magnetic resonance, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, and ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy confirmed the successful synthesis of the functionalised HA. Control over both the NO donor and HA concentrations allowed for the preparation of NO-releasing, HA-based nanofibers of varying diameters (240–490 nm), NO payloads (10–620 nmol mg−1), maximum amounts of NO released (160–8920 ppb mg−1), and NO release durations (1.5–20.2 h). Moreover, the NO-releasing nanofibers had good biodegradability and potential wound healing effects without any observed cytotoxicity. The biodegradable and NO-releasing HA-based nanofibers developed in this study have the potential application in wound healing.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...