In situ synthesis of fluorescent polydopamine on biogenic MnO2 nanoparticles as stimuli responsive multifunctional theranostics†
Abstract
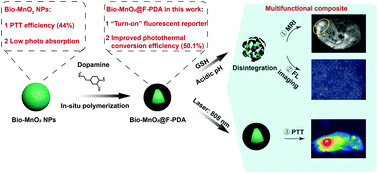
Multifunctional nanocomposites have drawn great attention in clinical applications because of their ability to integrate diagnostic and therapeutic functions. Manganese dioxide (MnO2), owing to its biocompatibility and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) properties, has been widely applied in biomedical research. Our previous work on biogenic MnO2 nanoparticles (Bio-MnO2 NPs) revealed that intrinsic photothermal properties and stimuli-responsive MRI imaging are particularly promising for the development of theranostic systems. However, further improvement in the photothermal therapy (PTT) performance of Bio-MnO2 NPs is still required. Herein, we have improved the PTT efficiency of Bio-MnO2 NPs by in situ synthesis of fluorescent polydopamine (PDA) while generating additional stimuli responsive fluorescence properties in this system, thus further broadening the scope of their theranostic functions. These synthesis conditions are mild and green. The fluorescence of PDA was quenched by capping Bio-MnO2 NPs and could be recovered upon degradation of Bio-MnO2 NPs inside tumour cells. Additionally, Mn2+ released from the nanoparticles can support T1-weighted MR imaging. Compared to the Bio-MnO2 NPs alone, the integration of Bio-MnO2 NPs and PDA significantly enhances the photothermal performance in vitro and in vivo. With their high biocompatibility, these multifunctional composite nanodevices hold great potential for fluorescence imaging and MRI-guided photothermal therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...