Heparin modulates the cellular uptake of nanomedicines†
Abstract
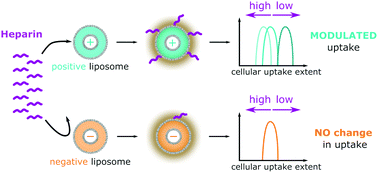
Liposomal formulations are used to improve the safety and cellular absorption of conventional drugs by limiting their interaction with phagocytes. The uptake behaviour of these nanocarriers is affected by the blood composition, and accordingly the presence of an anticoagulant in the blood could have a critical impact on the efficiency of nanomedicines. For the negatively charged liposomes, such as AmBisome®, no significant change in the uptake could be observed when co-incubated with heparin and primary phagocytes. Yet, we observed that a peak of the uptake extent of cationic liposomes was reached at a clinically relevant concentration of heparin for phagocytes and cancer cells. Hence, we recommend avoiding treatment of a heparinized patient with cationic nanomedicines because unexpectedly high uptake can occur in phagocytes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...