Tailoring the cationic lipid composition of lipo-DVDMS augments the phototherapy efficiency of burn infection†
Abstract
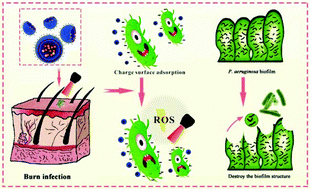
Increase in infections with Gram-negative Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) is a serious global challenge in healthcare. Sinoporphyrin sodium (DVDMS) combined with photodynamic antimicrobial chemotherapy (PACT) can effectively eradicate Gram-positive organisms. However, the poor penetration of DVDMS into the Gram-negative bacterial cell membrane and bacterial biofilm greatly limits the photo-inspired antimicrobial activity. This study optimized the cationic lipid-mediated nano-DVDMS delivery to improve the cellular uptake, and evaluated the antimicrobial efficacy of cationic DVDMS-liposome (CDL)-provoked PACT in both P. aeruginosa and its multidrug resistant strain. The results showed that the positively charged liposome modification promoted the enrichment of DVDMS in Gram-negative bacteria. CDL-PACT-produced ROS and caused bacterial death, accompanied by the decreased expression levels of virulence factor-related genes. The P. aeruginosa-infected burn model indicated satisfactory bacterial eradication and accelerated wound healing after CDL-PACT, in addition to gradually increasing bFGF, VEGF, TGF-β1 and Hyp levels and reducing TNF-α and IL-6, with no detectable side-effects. Overall, these findings provide fundamental knowledge that enables the design of feasible and efficient PACT treatments, including biophysical membrane permeabilization and photodynamic eradication, which are promising to overcome the infection and resistance of highly opportunistic Gram-negative bacteria.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...