Multivalent nanobody–biotin amplified enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the environmental detection of 3-phenoxybenzoic acid
Abstract
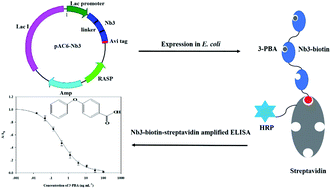
The 3-phenoxybenzoic acid (3-PBA) metabolized from pyrethroids is more toxic and has a longer half-life to degradation in a natural environment compared to its parent compounds. Few reports have focused on the environmental detection of 3-PBA. In this study, anti-3-PBA nanobodies in trivalent form (Nb3) were biotinylated. A sensitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) based on the combination of Nb3–biotin and streptavidin–horseradish peroxidase (SA–HRP) was developed for the environmental detection of 3-PBA. After optimization, the ELISA showed a half-maximum signal inhibition concentration (IC50) of 0.39 ng mL−1 in phosphate-buffered saline (pH 7, 20% MeOH) and a limit of detection (LOD) of 0.02 ng mL−1, which was more sensitive than the parent Nb-based ELISAs with IC50 and LOD values of 1.4 ng mL−1 and 0.1 ng mL−1, respectively. The Nb3–biotin amplified assay showed negligible cross-reactivity with its structural analogues (<0.1%). The average recoveries of 3-PBA from spiked canal water and soil samples ranged from 86.54–109.25% at 0.5–50 ng mL−1 (or ng g−1 (dw)). The 3-PBA residues in canal water and soil samples determined using this assay were in the ranges <LOD–1.46 ng mL−1 and <LOD–4.35 ng g−1 (dw), respectively, which correlated well with the results obtained using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. The results suggest that multivalent Nb–biotin–SA amplified ELISA is a promising tool for the routine environmental screening of 3-PBA.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...