Detection of Epstein–Barr virus by a rapid and simple accelerated denaturation bubble-mediated strand exchange amplification method†
Abstract
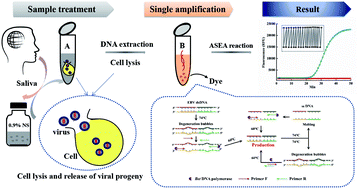
Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV) is a tumor-associated virus naturally transmitted through saliva. This virus is the pathogen of infectious mononucleosis, which is closely related to the occurrence of nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) and childhood lymphoma. Although a majority of EBV infected individuals exhibited good tolerance after primary infection, those who carry a viral load greater than the clinical cutoff value (COV), the upper level in healthy carriers, still suffer a high risk of cancer. Herein, a simple, rapid, and effective method, accelerated strand exchange amplification (ASEA), was developed for EBV detection, which could offer a strategy for non-invasive testing of EBV in saliva samples instead of blood samples as in traditional serology based methods and avoid bleeding during diagnosis. This approach could distinguish the genomic DNA of EBV and other species in saliva, and its limit of detection was as low as 1000 copies per mL, which was lower than the COV of EBV. Moreover, DNA extracted from saliva samples (n = 50) was employed as a template for EBV detection via qPCR and ASEA, the result of which showed that ASEA exhibited comparable sensitivity and specificity for actual sample diagnosis. Additionally, similar to conventional PCR, this method requires only one pair of primers and could be performed using a conventional fluorescence instrument, which makes this method easy to accomplish. Therefore, this rapid and effective method has the potential to provide rapid screening platforms for individuals with a high EBV load.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...