A high sensitivity electrochemical sensor based on a dual-template molecularly imprinted polymer for simultaneous determination of clenbuterol hydrochloride and ractopamine†
Abstract
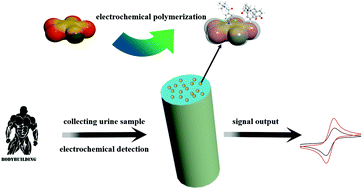
A nitrogen-doped Fe-MOF shows a high specific surface area and excellent electrical conductivity after high temperature carbonization. A novel electrochemical sensor based on a N@Fe-MOF@C loaded dual-template molecularly imprinted polymer (DTMIP) modified glassy carbon electrode (GCE) was proposed for the rapid and ultra-sensitive simultaneous detection of clenbuterol hydrochloride (CLB) and ractopamine (RAC). N@Fe-MOF@C combined with a MIP significantly enhanced the electrical signal. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) was used to detect CLB and RAC. The electrochemical polymerization was conducted with O-phenylenediamine as the functional monomer and CLB and RAC as template molecules. The factors affecting the sensor response were optimized. Under the optimal experimental conditions, the CV current response showed a linear range of 10−12–8 × 10−9 M for both CLB and RAC, and the detection limit (LOD) for both CLB and RAC was 3.03 × 10−13 M (S/N = 3). This electrochemical sensing system has high sensitivity, selectivity, excellent reproducibility, repeatability and stability. The recoveries of the actual samples (97.4%–101.2%) and reasonable relative standard deviations (RSDs) (1.06%–3.17%) indicate the practicability of the sensor system. The system has high application value in the rapid detection of CLB and RAC in clenbuterol hydrochloride tablets, human urine and raw pork.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...