Comparison of photoactivatable crosslinkers for in-gel immunoassays†
Abstract
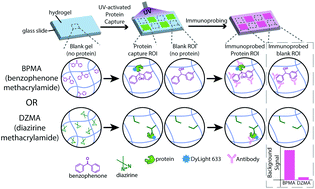
While fluorescence readout is a key detection modality for hydrogel-based immunoassays, background fluorescence due to autofluorescence or non-specific antibody interactions impairs the lower limit of detection of fluorescence immunoassays. Chemical modifications to the hydrogel structure impact autofluorescence and non-specific interactions. Benzophenone is a common photoactivatable molecule, and benzophenone methacrylamide (BPMA) has been used for cross-linking protein in polyacrylamide (PA) hydrogels. However, previous studies have suggested that the aromatic structure of benzophenone can contribute to increased autofluorescence and non-specific hydrophobic interactions with unbound fluorescent probes. Here, we synthesize diazirine methacrylamide (DZMA) as an alternative photoactivatable molecule to crosslink into PA hydrogels for in-gel protein capture for in-gel immunoassays. We hypothesize that the less hydrophobic structure of diazirine (based on previously reported predicted and experimental log P values) exhibits both reduced autofluorescence and non-specific hydrophobic interactions. We find that while equal concentrations of DZMA and BPMA result in lower protein target photocapture in the diazirine configuration, increasing the DZMA concentration up to 12 mM improves in-gel protein capture to be on par with previously reported and characterized 3 mM BPMA hydrogels. Furthermore, despite the higher concentration of diazirine, we observe negligible autofluorescence signal and a 50% reduction in immunoassay fluorescence background signal in diazirine gels compared to BPMA gels resulting in comparable signal-to-noise ratios (SNR) of the probed protein target. Finally, we test the utility of DZMA for single-cell immunoblotting in an open microfluidic device and find that protein migrates ∼1.3× faster in DZMA hydrogels than in BPMA hydrogels. However, in DZMA hydrogels we detect only 15% of the protein signal compared to BPMA hydrogels suggesting that the diazirine chemistry results in greater protein losses following electrophoretic separations. We establish that while diazirine has lower background fluorescence signal, which may potentially improve immunoassay performance, the lower capture efficiency of diazirine reduces its utility in open microfluidic systems susceptible to sample losses.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...