An artificial enzyme cascade amplification strategy for highly sensitive and specific detection of breast cancer-derived exosomes†
Abstract
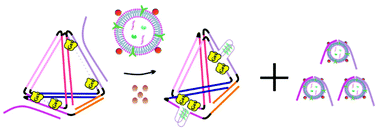
Tumor-related exosomes, which are heterogeneous membrane-enclosed nanovesicles shed from cancer cells, have been widely recognized as potential noninvasive biomarkers for early cancer diagnosis. Herein, an artificial enzyme cascade amplification strategy based on a switchable DNA tetrahedral (SDT) scaffold was proposed for quantification of breast cancer-derived exosomes. The SDT scaffold is composed of G-quadruplex mimicking DNAzyme sequences on its two single-stranded edges and glucose oxidase (GOx) on the four termini of the complementary strands. In the initial state, the SDT scaffold is blocked by the switch strand which consists of partial complementary domains with the DNA tetrahedron and a MUC1 aptamer. MCF-7 exosomes could release the quadruplex-forming sequences through the recognition of the MUC1 aptamer. The newly formed DNAzyme brings GOx into spatial proximity and induces high-efficiency enzyme cascade catalytic reactions on the SDT. Consequently, high sensitivity toward MCF-7 exosome analysis was obtained with a wide linear range of 3.8 × 106 to 1.2 × 108 particles per mL and a limit of detection of 1.51 × 105 particles per mL. In addition, such a DNAzyme reconfiguration strategy was able to distinguish MCF-7 exosomes from other breast cancer cell derived exosomes, indicating its excellent method specificity. The proposed enzyme cascade strategy not only provides a novel signal transformation and amplification nanoplatform for quantifying the specific populations of exosomes, but also can be further expanded to the analysis of multiple cancer biomarkers.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...