Differential detection of immune cell activation by label-free radiation pressure force
Abstract
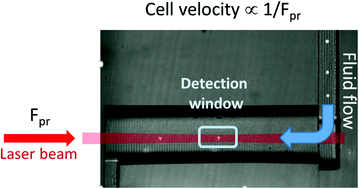
Label-free radiation pressure force analysis using a microfluidic platform is applied to the differential detection of innate immune cell activation. Murine-derived peritoneal macrophages (IC-21) are used as a model system and the activation of IC-21 cells by lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and interferon gamma (IFN-γ) to M1 pro-inflammatory phenotype is confirmed by RNA gene sequencing and nitric oxide production. The mean cell size determined by radiation pressure force analysis increases slightly after the activation (4 to 6%) and the calculated percentage of population overlaps between the control and the activated group after 14 and 24 h stimulations are at 79% and 77%. Meanwhile the mean cell velocity decreases more significantly after the activation (14% to 15%) and the calculated percentage of population overlaps between the control and the activated group after 14 and 24 h stimulations are only at 14% and 13%. The results demonstrate that the majority of the activated cells acquire a lower velocity than the cells from the control group without changes in cell size. For comparison label-free flow cytometry analysis of living IC-21 cells under the same stimulation conditions are performed and the results show population shifts towards larger values in both forward scatter and side scatter, but the calculated percentage of population overlaps in all case are significant (70% to 83%). Cell images obtained during radiation pressure force analysis by a CCD camera, and by optical microscopy and atomic force microscopy (AFM) reveal correlations between the cell activation by LPS/IFN-γ, the increase in cell complexity and surface roughness, and enhanced back scattered light by the activated cells. The unique relationship predicted by Mie's theory between the radiation pressure force exerted on the cell and the angular distribution of the scattered light by the cell which is influenced by its size, complexity, and surface conditions, endows the cell velocity based measurement by radiation pressure force analysis with high sensitivity in differentiating immune cell activation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...