A facile aptamer immobilization strategy to fabricate a robust affinity monolith for highly specific in-tube solid-phase microextraction†
Abstract
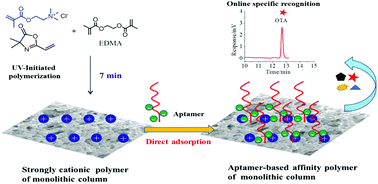
Developing a functional affinity monolithic column towards in-tube solid-phase microextraction (IT-SPME) for selective sample pretreatment is critical. Herein, a high-performance capillary affinity monolithic column with an ultra-high aptamer coverage density was rapidly fabricated via a simple adsorption strategy, in which aptamers with natural sequences were directly immobilized on an ammonium-based strongly cationic matrix. Limitations of the traditional biological or covalent methods such as time-consuming modification reactions, special requirement of active groups (e.g. –NH2 and –SH) on the aptamer, and low aptamer coverage density levels were avoided. An ultra-high coverage density of 8616 pmol μL−1 was achieved with excellent stability, and the highest aptamer-modification level among all the current methods was reached. Selective recognition and high recovery yields of the model mycotoxin ochratoxin A (OTA) were achieved in 95.9 ± 0.98%–97.9 ± 0.28% (n = 3). In particular, there was little cross-reactivity towards the OTB analogue of only 0.5% even in the case of 250 fold of the analogue OTB, which was not reported in previous affinity monoliths. Upon sample analysis, satisfactory discriminations of trace OTA were obtained at 93.7 ± 1.4%–95.5 ± 2.5% (n = 3) in beer and wheat. A facile and direct method for efficiently fabricating an aptamer-based affinity monolith towards online selective IT-SPME was proposed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...