Observation of inflammation-induced mitophagy during stroke by a mitochondria-targeting two-photon ratiometric probe†
Abstract
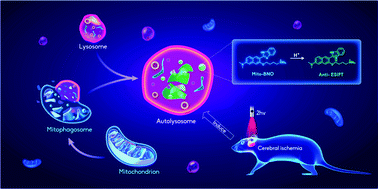
This study reports the development of a new, pH-sensitive, mitochondria-targeting two-photon ratiometric probe (Mito-BNO) for real-time tracking of mitophagy, a process that can be accelerated in brain tissue during stroke. Mito-BNO shows excellent capability for mitochondrial localisation (Pearson's correlation coefficient, r = 0.91), and can also effectively distinguish mitochondria from other subcellular organelles such as lysosomes and the endoplasmic reticulum (r = 0.40 and r = 0.33, respectively). Meanwhile, a rewarding pKa value (5.23 ± 0.03) and the pH reversibility suggest that Mito-BNO can track mitophagy in real time via confocal imaging. Most importantly, the relationship between mitophagy and neuroinflammation during stroke has been successfully demonstrated by evaluating the fluorescence of PC12 cells stained with Mito-BNO during an oxygen–glucose deprivation/reperfusion (OGD/R) process with and without anti-inflammatory treatment. The results indicate that the occurrence of mitophagy during stroke is caused by oxidative stress induced by neuroinflammation. This study will help further understanding stroke pathogenesis, can provide potential new targets for early diagnosis and treatment, and can also help to develop therapeutic drugs for stroke.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...