Fluorescence assay based on the thioflavin T-induced conformation switch of G-quadruplexes for TET1 detection†
Abstract
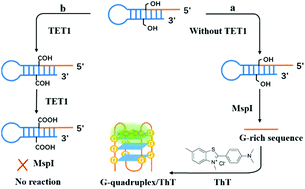
Ten-eleven translocation (TET) dioxygenase is of great significance in cytosine demethylation and in the control of cell differentiation and transformation. Herein, a fluorescence method has been developed for the highly sensitive detection of TET1, a member of the TET dioxygenase family. Based on the ThT-induced specific conformation of the G-quadruplex structure, the fluorescence signal decreased linearly with increasing TET1 concentration. The method shows potential clinical applications in the screening of TET protein inhibitors for anticancer drug discovery.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...