Carbon dots derived from kanamycin sulfate with antibacterial activity and selectivity for Cr6+ detection†
Abstract
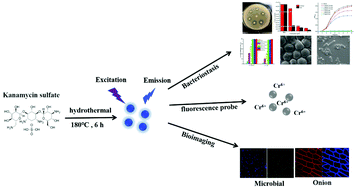
Among antibacterial nanomaterials, carbon dots (CDs) have attracted much attention because of their unique physical and chemical properties and good biosafety. In this study, kanamycin sulfate (Kan), a broad-spectrum antibiotic, was used to synthesize novel carbon dots (CDs-Kan) by a one-step hydrothermal method. CDs-Kan showed good inhibitory effects on Gram-negative Escherichia coli and Gram-positive Staphylococcus aureus. Further, scanning electron microscopy revealed that treatment with CDs-Kan and Kan resulted in the same phenomena. In particular, the morphologies of S. aureus cells treated with CDs-Kan and Kan became smaller and irregular, whereas the surfaces of E. coli cells protruded and formed vesicles. These results indicated that CDs-Kan was shown to retain the good antibacterial activity of Kan as well as its main bactericidal functional groups, namely, the amino sugar and amino cyclic alcohol, We refer to this phenomenon as the “preservation property”. We also found that CDs-Kan has good biocompatibility and nontoxic properties. Moreover, CDs-Kan was successfully applied to the biological imaging of fungi and plant cells. In addition, CDs-Kan could be used as a fluorescent probe for the quick, sensitive, and selective detection of Cr6+. Therefore, CDs-Kan not only retained the good bacteriostatic properties of Kan but also expanded its application in bioimaging and biosensors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...