Fe3O4@polydopamine and Exo III-assisted homogeneous biorecognition reaction for convenient and ultrasensitive detection of kanamycin antibiotic†
Abstract
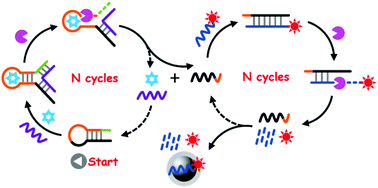
Herein, we report a Fe3O4@polydopamine (PDA) nanocomposite and exonuclease III (Exo III)-assisted homogeneous fluorescence biosensing method for ultrasensitive detection of kanamycin (Kana) antibiotic. A hairpin DNA containing the Kana-aptamer sequence (HP) was first designed for the highly specific biorecognition of the target analyte. Because of the aptamer biorecognition-induced structural change of HP and the highly effective catalyzed reaction of Exo III, a large amount of fluorophore labels were released from the designed fluorescence DNA probe. During the homogeneous reaction process, the Exo III-assisted dual recycling significantly amplified the fluorescence signal output. Moreover, the excessive probes were easily adsorbed and separated by the Fe3O4@PDA nanocomposite, which decreased the background signal and increased the signal-to-noise ratio. These strategies result in the excellent analytical performance of the method, including a very low detection limit of 0.023 pg mL−1 and a very wide linear range of six orders of magnitude. In addition, this method has convenient operation, excellent selectivity, repeatability and satisfactory reliability, and does not involve the design and utilization of complicated DNA sequences. Thus, it exhibits a promising prospect for practical applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...