Effect of proteins on the oxidase-like activity of CeO2 nanozymes for immunoassays†
Abstract
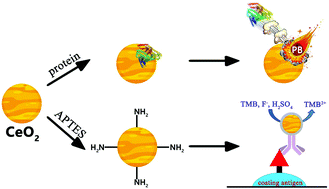
Having the benefits of low cost, excellent stability and tolerance to extreme conditions, nanozymes are a potential alternative of horseradish peroxidase (HRP) or other enzymes for bioanalytical chemistry, especially immunoassays. CeO2 nanoparticles have oxidase-mimicking activity and can avoid the use of unstable H2O2. For robust assays, the effect of proteins on the activity of CeO2 needs to be carefully studied. Herein, we studied the adsorption and desorption of bovine serum albumin (BSA) from CeO2. The CeO2 nanoparticles exhibited a higher protein adsorption capacity compared to the other tested metal oxide nanoparticles. Although the oxidase-like activity of CeO2 was inhibited by BSA, low concentrations of phosphate and fluoride ions boosted the activity of protein-capped CeO2. CeO2 was still active under strong acidic conditions and at high temperature, while HRP lost its activity. For immunoassay development, we covered CeO2 with an amine-modified silane for covalent conjugation to antibodies. A one-step indirect competitive ELISA for fenitrothion was developed, and an IC50 value of 35.6 ng mL−1 and a limit of detection of 2.1 ng mL−1 were obtained.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...