Fe–N/C single-atom nanozyme-based colorimetric sensor array for discriminating multiple biological antioxidants†
Abstract
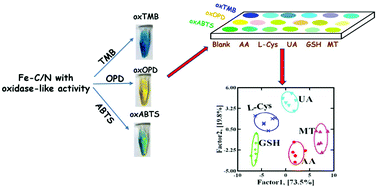
Identifying the species and concentrations of antioxidants is really important because antioxidants play important roles in various biological processes and numerous diseases. Compared with an individual sensor detecting a single antioxidant with limited specificity, a sensor array could simultaneously identify various antioxidants, in which 3–5 types of nanomaterials with peroxidase-like activity are absolutely necessary. Herein, as a single-atom nanozyme, Fe–N/C with oxidase-mimicking activity was applied to construct a triple-channel colorimetric sensor array: (1) Fe–N/C catalytically oxidized three substrates 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB), 2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (ABTS) and o-phenylenediamine (OPD) to produce blue oxidized TMB (oxTMB), green oxidized ABTS (oxABTS) and yellow oxidized OPD (oxOPD), respectively; (2) with oxTMB, oxABTS and oxOPD as three sensing channels, a colorimetric sensor array was constructed for simultaneously discriminating glutathione (GSH), L-cysteine (L-Cys), ascorbic acid (AA), uric acid (UA), and melatonin (MT), even quantifying concentrations (with GSH as a model analyst). The performance of the sensor array was validated through accurately identifying 15 blind samples containing GSH, L-Cys, AA, UA and MT in buffer solution and human serum samples, and also in binary and ternary mixtures. This work proved that fabricating a single nanozyme-based sensor array was a simplified and reliable strategy for simultaneously probing multiple antioxidants.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...