The role of third cation doping on phase stability, carrier transport and carrier suppression in amorphous oxide semiconductors†
Abstract
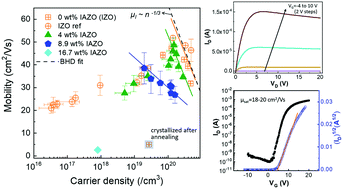
Amorphous oxide semiconductors (AOSs), specifically those based on ternary cation systems such as Ga-, Si-, and Hf-doped InZnO, have emerged as promising material candidates for application in next-gen transparent electronic and optoelectronic devices. Third cation-doping is a common method used during the manufacturing of amorphous oxide thin film transistors (TFTs), primarily with the intention of suppressing carrier generation during the fabrication of the channel layer of a transistor. However, the incorporation of a third cation species has been observed to negatively affect the carrier transport properties of the thin film, as it may act as an additional scattering center and subsequently lower the carrier mobility from ∼20–40 cm2 V−1 s−1 of In2O3 or a binary cation system (i.e., InZnO) to ∼1–10 cm2 V−1 s−1. This study investigates the structural, electrical, optoelectronic, and chemical properties of the ternary cation material system, InAlZnO (IAZO). The optimized carrier mobility (Hall Effect) of Al-doped InZnO is shown to remain as high as ∼25–45 cm2 V−1 s−1. Furthermore, Al incorporation in InZnO proves to enhance the amorphous phase stability under thermal stresses when compared to baseline InZnO films. Thin film transistors integrating optimized IAZO as the channel layer are shown to demonstrate promisingly high field effect mobilities (∼18–20 cm2 V−1 s−1), as well as excellent drain current saturation and high drain current on/off ratios (>107). The high mobility and improved amorphous phase stability suggest strong potential for IAZO incorporation in the next generation of high performance and sustainable optoelectronic devices such as transparent displays.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...