Ultra-high lattice thermal conductivity and the effect of pressure in superhard hexagonal BC2N
Abstract
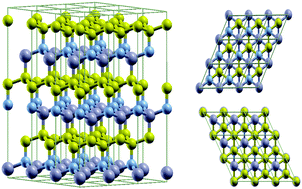
Hexagonal BC2N is a superhard material recently identified to be comparable to or even harder than cubic boron nitride (c-BN) due the full sp3 bonding character and the higher number of C–C and B–N bonds compared to C–N and B–C. Using a first-principles approach to calculate force constants and an exact numerical solution to the phonon Boltzmann equation, we show that BC2N has a high lattice thermal conductivity exceeding that of c-BN owing to the strong C–C and B–N bonds, which produce high phonon frequencies as well as high acoustic velocities. The existence of large group velocities in the optical branches is responsible for its large thermal conductivity. Its coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) is found to match that of Si above 400 K The combination of large thermal conductivity and a good CTE match with that of Si, makes BC2N a promising material for use in thermal management and high-power electronics applications. We show that the application of compressive strain increases the thermal conductivity significantly. This enhancement results from the overall increased frequency scale with pressure, which makes acoustic and optic velocities higher, and weaker phonon–phonon scattering rates.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...