Laser induced ultrafast combustion synthesis of solution-based AlOx for thin film transistors†
Abstract
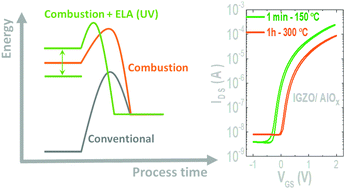
Solution processing of amorphous metal oxides using excimer laser annealing (ELA) has been lately used as a viable option to implement large-area electronics, offering high quality materials at a reduced associated cost and process time. However, the research has been focused on semiconductor and transparent conductive oxide layers rather than on the insulator layer. In this work we present amorphous aluminum oxide (AlOx) thin films produced at low temperature (≤150 °C) via combustion synthesis triggered by ELA, for oxide thin film transistors (TFTs) suitable for manufacturing flexible electronics. The study showed that combining ELA and combustion synthesis leads to an improvement in the dielectric thin film's densification in a shorter time (≤15 min). Optimized dielectric layers were obtained combining a short drying cycle at 150 °C followed by ELA treatment. High breakdown voltage (4 MV cm−1) and optimal dielectric constant (9) was attained. In general, TFT devices comprising the AlOx fabricated with a drying cycle of 15 min followed by ELA presented great TFT properties, a high saturation mobility (20.4 ± 0.9 cm2 V−1 s−1), a small subthreshold slope (0.10 ± 0.01 V dec−1) and a turn-on voltage ∼0 V. ELA is shown to provide excellent quality solution-based high-κ AlOx dielectric, that surpass other methods, like hot plate annealing and deep ultraviolet (DUV) curing. The results achieved are promising and expected to be of high value to the printed electronic industry due to the ultra-fast film densification and the surface/area selective nature of ELA.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...