Interfacial strain driven magnetoelectric coupling in (111)-oriented self-assembled BiFeO3–CoFe2O4 thin films
Abstract
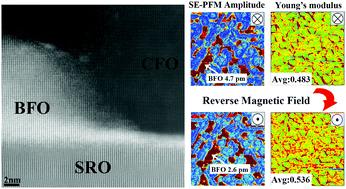
Magnetoelectric materials have been considered as promising candidates for data storage and sensors based on spintronic technology. Multiferroic BiFeO3–CoFe2O4 (BFO–CFO) epitaxial thin films deposited on a (111)-oriented SrTiO3 substrate exhibit ferromagnetism, piezoelectricity and strong magnetoelectric properties simultaneously. Interfacial strain between two phases plays a key role in such unique characters. Thus, strain engineering is a good method to enhance the magnetoelectric coupling effect. Here, to clearly understand the role of strain for further strain engineering, the interfacial strain between BFO and CFO and its evolution under electric/magnetic fields are investigated. This work semiquantitatively establishes a detailed relationship between the magnetoelectric coupling effect and interfacial strains – the piezoelectric amplitude drops by 44.7% and meanwhile the out-of-plane tensile strain rises by 11.0% under magnetic fields. This finding is helpful in optimizing multiferroic composite structures and achieving wider applications in future.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...