Saturated red iridium(iii) complexes containing a unique four-membered Ir–S–C–N backbone: mild synthesis and application in OLEDs†
Abstract
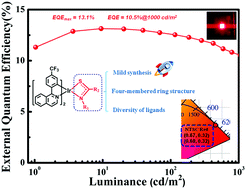
A series of new iridium(III) cyclometalated complexes (4tfmpiq)2Ir(tiptha), (4tfmpiq)2Ir(phdiptha), (4tfmpiq)2Ir(fphdiptha) and (4tfmpiq)2Ir(ipdptha) (4tfmpiq = 4-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)isoquinoline, tiptha = 1,1,3-triisopropylthiourea, phdiptha = 1,1-diisopropyl-3-phenylthiourea, fphdiptha = 3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1,1-diisopropylthiourea, ipdptha = 3-isopropyl-1,1-diphenylthiourea) containing a unique four-membered ring Ir–S–C–N backbone were facilely synthesized under mild conditions. By introducing different substituents such as isopropyl, phenyl, 4-fluorophenyl, diisopropylamine and diphenylamine on the thiourea ancillary ligands, not only the S–C–N ligands can be extensively derived, but also the emission colors (λpeak = 627–636 nm) and photoluminescence quantum efficiencies (ΦP = 38.0–42.0%) can be regulated. Employing these complexes as emitters, the organic light emitting diodes (OLEDs) exhibited good performances with a maximum external quantum efficiency (EQEmax) of 13.1% for saturated red emission with CIE coordinates of (0.68, 0.32). These results demonstrate the great potential of the S–C–N ancillary ligands for developing new Ir(III) complexes towards OLED applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...