Conjugation of biphenyl groups with poly(ethylene glycol) to enhance inhibitory effects on the PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint interaction†
Abstract
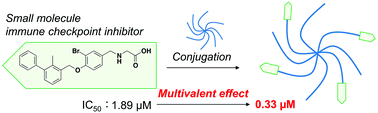
Monoclonal antibodies have been developed as anticancer agents to block immune checkpoint pathways associated with programmed cell death 1 (PD-1) and its ligand PD-L1. However, the high cost of antibodies has encouraged researchers to develop other inhibitor types. Here, biphenyl compounds were conjugated with poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) to enhance the activity of small molecular inhibitors. Immunoassay results revealed the decrease in the inhibition activity following conjugation with linear PEG, suggesting that the PEG moiety reduced the interaction between the biphenyl structure and PD-L1. However, the inhibitory effect on PD-1/PD-L1 interaction was further enhanced by using branched PEG conjugates. The increase in the number of conjugated biphenyl compounds resulted in increased inhibitory activity. The highest IC50 value was 0.33 μM, which was about 5 times higher than that observed for a non-conjugated monovalent compound. The inhibitory activity was more than 20 times the activity reported for the starting compound. Considering the increase in the inhibition activity, this multivalent strategy can be useful in the design of new immune checkpoint inhibitors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...