Dual-path modulation of hydrogen peroxide to ameliorate hypoxia for enhancing photodynamic/starvation synergistic therapy†
Abstract
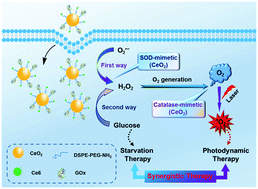
The common existence of hypoxia within the tumor microenvironment severely restricts the efficacy of photodynamic therapy (PDT), which is attributed to the fact that the PDT process is strongly oxygen (O2) dependent. Here, a multifunctional composite (named CPCG), which combines polyethylene glycol (PEG) functionalized cerium oxide nanoparticles (CeO2) with photosensitizer chlorin e6 (Ce6) and glucose oxidase (GOx), is reported for generating O2 within the tumor microenvironment by the dual-path hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-modulated ways to ameliorate hypoxia, thereby enhancing the PDT efficiency. This process is realized based on the dual enzyme-like activity of CeO2. The first modulated way is to transform the superoxide anion (O2˙−) into H2O2 by the superoxide dismutase-like activity of CeO2. The second modulated way is to decompose glucose into H2O2 through the catalysis of GOx. Subsequently, H2O2 generated from the above dual modulated ways can further produce O2via the catalase-like activity of CeO2. Additionally, the depletion of glucose could impede the nutrient supply to obtain starvation therapy. Both in vitro and in vivo experiments indicate that the CPCG composite could enhance the efficacy of photodynamic/starvation synergistic therapy. Therefore, this strategy offers great potential to modulate the O2 level in the tumor microenvironment for better therapeutic outcomes, and can act as a promising candidate in photodynamic/starvation synergistic therapy.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...