Ferrocene-modified peptides as inhibitors against insulin amyloid aggregation based on molecular simulation†
Abstract
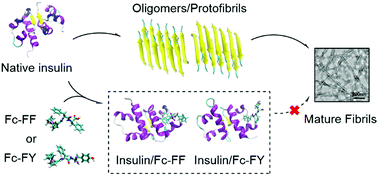
Peptide-based inhibitors have gradually been implicated as drugs for treating protein folding diseases because of their favorable biocompatibility and low toxicity. To develop potential therapeutic strategies for amyloid-related disorders, short peptides modified by Fc, ferrocene-L-Phe-L-Phe (Fc-FF) and ferrocene-L-Phe-L-Tyr (Fc-FY), were used as inhibitors for the investigation of the aggregation behavior of insulin. Firstly, molecular docking predicted the interaction between both Fc-peptides and insulin. Then, the experimental data from ThT, DLS, CD and TEM confirmed that Fc-FF and Fc-FY effectively inhibited insulin fibrillation and disaggregated mature insulin fibrils. Based on a dose-dependent manner, both Fc-peptides can strongly inhibit insulin fibrillation, extend lag phase time, reduce final fibril formation (beyond 99% by Fc-peptides of 400 µM), decrease the formation of high-content β-sheet structures and reduce the size of insulin fibrils. Additionally, we found that compared with Fc-FY, the better inhibitory effect of Fc-FF at concentration below 400 µM was mainly resulted from the difference in π–π interaction and hydrogen bonds between Fc-peptides and insulin, according to molecular dynamics analysis. Our results demonstrated Fc-peptides, Fc-FF and Fc-FY, may play effective roles in the development of new therapeutic drugs or strategies for amyloid-related disorders, and the molecular dynamics simulation may be helpful for designing appropriate inhibitors of anti-amyloidosis diseases.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...