Graphene–nucleic acid biointerface-engineered biosensors with tunable dynamic range†
Abstract
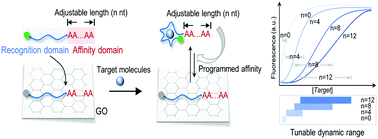
Programmed biosensors with tunable quantification range and sensitivity would greatly broaden their application in medical diagnosis, food safety and environmental analysis. Herein, we proposed a graphene–nucleic acid biointerface-engineered biosensor, allowing target molecules to be detected with adjustable dynamic ranges and sensitivities. The biosensors were programmed by simply tuning the poly A tail of aptamer probes. The tuning of the poly A tail would allow the interaction between aptamer probes and graphene oxide (GO) to be modulated, in turn programing the competitive binding processes of aptamer probes to target molecules and GO. The biosensors, termed affinity-tunable aptasensors (atAptasensors) could be easily tuned with different dynamic ranges by using aptamer probes with different tail lengths, and the dynamic range could be extended to be over 3 orders by a combined use of multiple aptamer probes. Remarkably, the specificity of aptamer probes could be increased by increasing the interaction between aptamer probes and GO. Reliability of atAptasensor for ATP detection was tested in serum and milk samples, and we also applied atAptasensor for culture-independent analysis of microorganism pollution.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Biosensors


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...