A portable chromogenic and fluorogenic membrane sensor for ultrasensitive, specific and instantaneous visualizing of lethal phosgene†
Abstract
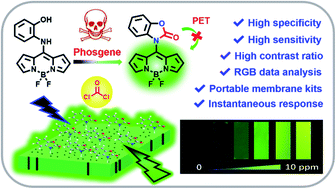
Phosgene is an indispensable industrial gas that has high toxicity, and has been used as a chemical warfare agent, meaning that it poses a great threat to public security in the case of accidental leakage or terrorist attack. To monitor toxic phosgene, herein, we devised a facile and reliable optical sensor (BODIPY–OHA) based on o-hydroxyaniline (OHA) and BODIPY. The adjacent hydroxyl and amino groups in OHA synergistically couple with phosgene to form benzoxazolinone, thus BODIPY–OHA displays a remarkable color change from light green to yellow and a synchronous fluorescence turn-on response towards phosgene. The sensor can be used to specifically sense phosgene, with some favorable merits such as instantaneous response, ultralow detection limit (0.22 nM), noticeable color and fluorescence changes, as well as a high signal-to-noise ratio. Furthermore, this sensor was fabricated as portable membrane strips to serve as an easy-to-handle kit for highly specific, instantaneous, sensitive and visual detection of gaseous phosgene. Moreover, a simple RGB pattern from the fluorescence of test strips was established to allow quantitative determination of the level of phosgene, which was successfully used to monitor the leakage of phosgene. Therefore, these test strips have great potential for monitoring phosgene in public places and industrial production in the case of accidental leakage or terrorist attack.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...