Electrostatic self-assembly of a AgI/Bi2Ga4O9 p–n junction photocatalyst for boosting superoxide radical generation†
Abstract
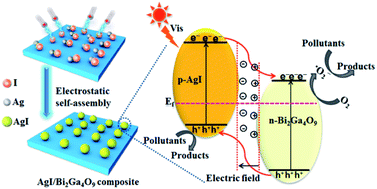
Semiconductor p–n junction engineering plays an indispensable role in developing highly efficient photocatalysts for energy conversion and environmental remediation. Herein, a novel AgI/Bi2Ga4O9 p–n junction photocatalyst is successfully constructed by an electrostatic self-assembly approach. Photoelectrochemical characterization together with density functional theory calculations shows that the formation of a p–n junction at the AgI/Bi2Ga4O9 interface favors separation and transfer of photogenerated charge carriers. The ˙O2− generated by 25%-AgI/Bi2Ga4O9 reaches a concentration of 18.8 μmol L−1 after 60 min of irradiation, which is 3.3 and 12.5 times higher than that generated by AgI and Bi2Ga4O9, providing 25%-AgI/Bi2Ga4O9 with greatly enhanced photocatalytic activity toward Acid Red 1 and metronidazole degradation. Our work provides a novel strategy for designing highly efficient photocatalysts for a wide range of energy and environmental applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...