Enhanced carrier separation and increased electron density in 2D heavily N-doped ZnIn2S4 for photocatalytic hydrogen production†
Abstract
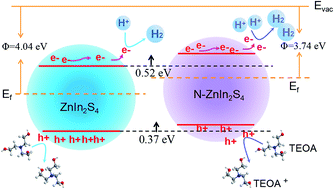
Element doping is an effective approach to modify photocatalysts for boosting solar H2 evolution, especially anion doping. However, there still exists controversy regarding the role of heavy doping in photocatalysis. Herein, 2D heavily N-doped ZnIn2S4 is reported based on an in-depth perspective on the role that N heteroatoms play in improving the photocatalytic properties. The electron dynamics was investigated via femtosecond transient absorption spectroscopy which revealed that the introduction of N doping in ZnIn2S4 provides a strong electron aggregation ability for improving the efficiency of charge separation. Meanwhile, the increased valence band width and the elevated conduction band, respectively, promote the mobility of holes and provide more reductive photogenerated electrons. As a result, 2D heavily N-doped ZnIn2S4 exhibited superior photocatalytic hydrogen production compared to the pristine ZnIn2S4. The optimal hydrogen evolution rate is 11 086 μmol g−1 h−1 under visible light irradiation. This work contributes to the improvement of photocatalytic performance in 2D ZnIn2S4 and provides an in-depth understanding of heteroatom doped photocatalysts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...