Variable pitch hydrodynamic electro-optic gratings utilising bent liquid crystal dimers†
Abstract
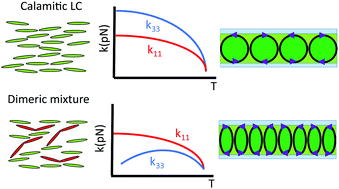
Electrohydrodynamic instabilities (EHDI) in liquid crystals form uniform and continuously variable diffractive structures when subject to certain material and geometry determined conditions. A one-dimensional grating is one such diffractive structure, where the refractive index changes periodically in a direction parallel to the initial liquid crystal director. The period of this structure has been shown previously to vary continuously between the values of the cell gap and half-cell gap approximately, allowing continuous angular modulation of optical beams but with a limited angular range. In this work, the lower pitch limit is shown to also be governed in part by the ratio of the splay and bend elastic constants (k11/k33) of the liquid crystal. A host nematic liquid crystal with standard elastic constant ratios (k11/k33 < 1) is doped with odd-alkyl-spaced dimeric liquid crystal CB7CB, to create a liquid crystal mixture with a far higher elastic constant ratio (k11/k33 > 5) than for those previously used in literature EHDI studies. The EHDI gratings formed in this new mixture exhibit pitch lengths significantly below half-cell gap, allowing up to 50% wider angle continuous steering of light. This improves the potential for application in beamsteering and diffractive optical devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...