A long side chain imidazolium-based graft-type anion-exchange membrane: novel electrolyte and alkaline-durable properties and structural elucidation using SANS contrast variation†
Abstract
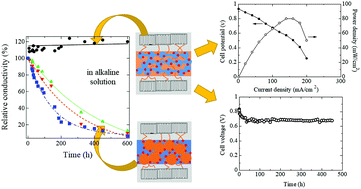
Newly designed styrylimidazolium-based grafted anion-exchange membranes (StIm-AEMs), in which imidazolium ionic groups are attached to styrene at the far side from the graft chains, were prepared by radiation-induced graft polymerization of p-(2-imidazoliumyl) styrene onto poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoloethylene) (ETFE) films, followed by N-alkylation and ion-exchange reactions. StIm-AEM having an ion exchange capacity (IEC) of 0.54 mmol g−1 with a grafting degree (GD) of ∼18%, possesses practical conductivity (>50 mS cm−1) even with a very low water uptake (∼10%) and high stability over 600 h in a 1 M KOH solution at 80 °C. There exists a critical IEC (IECc) in the range of 0.7–0.8 mmol g−1 over which the membrane showed high water uptake, which resulted in pronounced susceptibility to hydrolysis. Using small-angle neutron scattering technique with a contrast variation method, we found the hydrophilic phase in StIm-AEMs with IECs lower and higher than IECc shows “reverse-micelles” with water domains dispersed in the polymer matrix and “micelles” with graft polymer aggregates dispersed in the water matrix, respectively. The further analysis of micelle structures using the hard-sphere liquid model and Porod limit analysis reveals that the interfacial structures of ionic groups are essential for the electrochemical properties and durability of StIm-AEMs. In addition, StIm-AEM with an IEC of 0.95 mmol g−1 and the maximum power density of 80 mW cm−2 in the hydrazine hydrate fuel cell test, exhibited long-term durability under constant current (8.0 mA) up to 455 h, which, thus far, is the best durability at 80 °C for platinum-free alkaline-type liquid fuel cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...