Patchy rough colloids as Pickering stabilizers†
Abstract
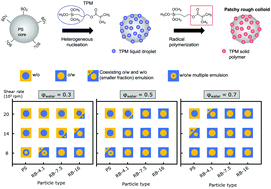
Pickering stabilizers are typically considered to be perfectly smooth and chemically homogeneous. The use of rough and heterogeneous colloids is expected to fundamentally alter the properties of emulsions. In particular, we investigate the role of surface structuring in the emulsification and catastrophic phase inversion of Pickering emulsions. To gain deeper fundamental insights into this topic, we fabricate in a controlled and simple manner patchy rough particles with a polystyrene core and organosilicate asperities. As a consequence of the synthesis, the surface roughness and chemical heterogeneity are coupled, namely the chemical heterogeneity is directly connected with the surface patchiness. The synthesis is robust, scalable and leads to the production of grams in less than a day. The geometrical roughness is characterized with AFM, while the chemical composition is extracted from oxidative mass loss upon combustion. Wetting studies are empirically carried out using a gel trapping technique and the results are compared with the theoretically derived contact angles of particles. Systematic variations in the emulsification shear rate, oil/water ratio and particle type reveal the influence of particle heterogeneity on the formation and formulation of emulsions. This work paves the way for a deeper understanding of the behavior of Pickering emulsions, where non-ideal, heterogeneous particles are present.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...