A solution blown superporous nonwoven hydrogel based on hydroxypropyl cellulose†
Abstract
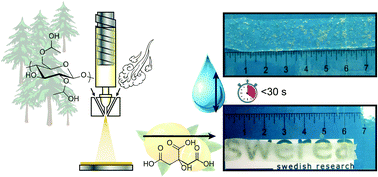
A superporous hydrogel – in which the interconnecting fibres themselves are hydrogels – based on hydroxypropyl cellulose (HPC) has been produced using the nonwoven solution blown technique. The nonwoven fibres were subsequently thermally crosslinked with citric acid as identified by esterbond formation using FT-IR spectroscopy. The gel fraction was approximately 70%. The superporous HPC hydrogel exhibited a very fast water absorption, reaching an equilibrium absorption (80% water content) within 30 seconds. The equilibrium absorption was strongly codependent on both the fibre thickness and the pore size whereas the absorption rate was correlated with the pore size as established using standard linearized regression analysis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...