Micellar growth and network formation in acidic solutions of a sulfobetaine zwitterionic surfactant triggered by an inorganic salt†
Abstract
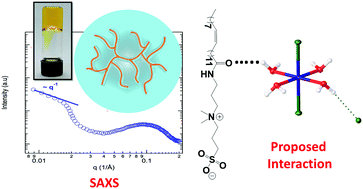
Micellization (formation of wormlike structures) of 3-(N-erucamidopropyl-N,N-dimethyl ammonium)propane sulfonate (EDAS) in the presence of an inorganic salt, iron chloride (FeCl3), in acidic conditions is studied using static and dynamic rheological measurements and small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS). Infrared spectroscopy, single crystal X-ray, and UV-visible spectroscopy are used to further investigate the mechanisms of viscosity and elasticity and the enhancement and formation of an elastic gel-like solution induced by Fe3+ in HCl. The nature of the interaction is characterized to be hydrogen bonding between the amide groups of EDAS and coordinated water in trans-[FeCl2(H2O)4]Cl structure. Such an interaction masks the repulsion forces between surfactant headgroups. This screening effect results in the formation of longer wormlike micelles in the solution. The chemical structure of FeCl3 in concentrated HCl was predicted in the literature through theoretical and experimental techniques; however, its crystal structure, including the exact geometry (e.g., cis or trans) and the non-coordinated chloride position is reported for the first time in the present study. The findings of this study show the sensitivity of a sulfobetaine zwitterionic surfactant to pH alteration and inorganic salt.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...