Kinetics of actin networks formation measured by time resolved particle-tracking microrheology†
Abstract
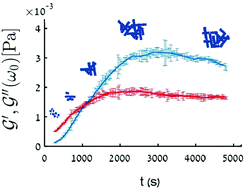
Actin is one of the most studied cytoskeleton proteins showing a very rich span of structures and functions. For example, adenosine triphosphate (ATP)-assisted polymerization of actin is used to push protrusions forward in a mechanism that enables cells to crawl on a substrate. In this process, the chemical energy released from the hydrolysis of ATP is what enables force generation. We study a minimal model system comprised of actin monomers in an excess of ATP concentration. In such a system polymerization proceeds in three stages: nucleation of actin filaments, elongation, and network formation. While the kinetics of filament growth was characterized previously, not much is known about the kinetics of network formation and the evolution of networks towards a steady-state structure. In particular, it is not clear how the non-equilibrium nature of this ATP-assisted polymerization manifests itself in the kinetics of self-assembly. Here, we use time-resolved microrheology to follow the kinetics of the three stages of self-assembly as a function of initial actin monomer concentration. Surprisingly, we find that at high enough initial monomer concentrations the effective elastic modulus of the forming actin networks overshoots and then relaxes with a −2/5 power law. We attribute the overshoot to the non-equilibrium nature of the polymerization and the relaxation to rearrangements of the network into a steady-state structure.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Active Matter


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...