Crossover from mean-field compression to collective phenomena in low-density foam-formed fiber material
Abstract
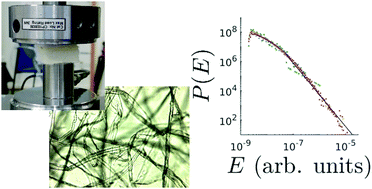
We study the compression of low-weight foam-formed materials made out of wood fibers. Initially the stress–strain behavior follows mean-field like response, related to the buckling of fiber segments as dictated by the random three-dimensional geometry. Our Acoustic Emission (AE) measurements correlate with the predicted number of segment bucklings for increasing strain. However, the experiments reveal a transition to collective phenomena as the strain increases sufficiently. This is also seen in the gradual failure of the theory to account for the stress–strain curves. The collective avalanches exhibit scale-free features both as regards the AE energy distribution and the AE waiting time distributions with both exponents having values close to 2. In cyclic compression tests, significant increases in the accumulated acoustic energy are found only when the compression exceeds the displacement of the previous cycle, which further confirms other sources of acoustic events than fiber bending.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...