Self-assembled toron-like structures in inverse nematic gels†
Abstract
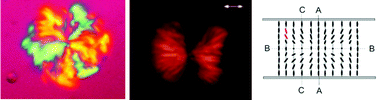
A novel form of nematic gel (N-gel) wherein bright flower-like domains (BFDs) rich in gelator fibres are embedded in a matrix of liquid crystal (LC) molecules has been reported. These gels which we denote as inverse N-gels are unlike typical N-gels in which the LC is encapsulated within an aggregated network of gelator molecules. The self-organization of the helical gelator fibres within the BFDs leads to the creation of localized toron-like structures that are topologically protected due to their skyrmion director profile. Optical and confocal microscopy have been used to deduce the LC director configuration, in order to understand possible intermolecular interactions that can lead to the formation of the twisted structures and the inverse N-gels.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...