High mobility of lattice molecules and defects during the early stage of protein crystallization†
Abstract
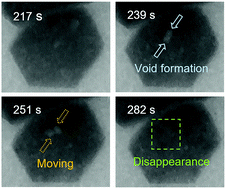
Protein crystals are expected to be useful not only for their molecular structure analysis but also as functional materials due to their unique properties. Although the generation and the propagation of defects during crystallization play critical roles in the final properties of protein crystals, the dynamics of these processes are poorly understood. By time-resolved liquid-cell transmission electron microscopy, we observed that nanosized crystal defects are surprisingly mobile during the early stages of the crystallization of a lysozyme as a model protein. This highly dynamic behavior of defects reveals that the lattice molecules are mobile throughout the crystal structure. Moreover, the disappearance of the defects indicated that intermolecular bonds can break and reform rapidly with little energetic cost, as reported in theoretical studies. All these findings are in marked contrast to the generally accepted notion that crystal lattices are rigid with very limited mobility of individual lattice molecules.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...