Solvation dynamics of N-substituted acrylamide polymers and the importance for phase transition behavior†
Abstract
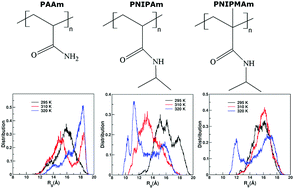
Functional groups present in thermo-responsive polymers are known to play an important role in aqueous solutions by manifesting their coil-to-globule conformational transition in a specific temperature range. Understanding the role of these functional groups and their interactions with water is of great interest as it may allow us to control both the nature and temperature of this coil-to-globule transition. In this work, polyacrylamide (PAAm), poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAm), and poly(N-isopropylmethacrylamide) (PNIPMAm) solvated in water are studied with the goal of discovering the structure of the solvent and its interaction with these polymers in determining the polymer conformations. Specifically, all-atom molecular dynamics (MD) simulations were performed on polymer chains with 30 monomer units (30-mers) at 295 K, 310 K and 320 K, which is below and above the lower critical solution temperature (LCST) of PNIPAm (LCST = 305 K) and PNIPMAm (LCST = 315 K), respectively. The MD simulation trajectories suggest that changes in the functional groups in the backbone and side-chains alter the water solvation shell around the polymer. This results in a change in the residence time probability and hydrogen bond characteristics of water at simulated temperatures. Specifically, water molecules reside for longer times near PAAm (no LCST) and PNIPMAm (LCST = 315 K) chains as compared to PNIPAm. This might be one of the possible causes for the higher LCST of PNIPMAm as compared to that of PNIPAm. These results can guide experimentalists and theoreticians to design new polymer structures with tailor-made LCST transitions while controlling the water solvation shell around the functional group.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...