Hollow C@TiO2 array nanospheres as efficient sulfur hosts for lithium–sulfur batteries†
Abstract
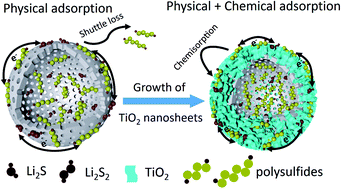
Herein, hollow core–shell C@TiO2 array nanospheres were synthesized as advanced sulfur hosts and realized much-improved electrochemical performance. Specifically, hollow buffer structures can encapsulate sulfur, while the polar TiO2 nanoarray is able to provide intense chemisorption towards polysulfides, synergistically easing the shuttle effect. Consequently, the C@TiO2/S cathode delivered a low fading rate of 0.055% per cycle for 500 cycles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...