Binding site exchange kinetics revealed through efficient spin–spin dephasing of hyperpolarized 129Xe†
Abstract
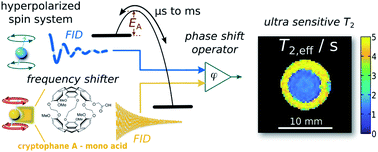
Spin exchange between different chemical environments is an important observable for characterizing chemical exchange kinetics in various contexts, including protein folding, chelation chemistry, and host–guest interactions. Such spins experience effective spin–spin relaxation rate, R2,eff, that typically shows a dispersive behavior which requires detailed analysis. Here, we describe a class of highly simplified R2,eff behavior by relying on hyperpolarized 129Xe as a freely exchanging ligand reporter. It provides large chemical shift separations that yield reduced expressions of both the Swift–Connick and the Carver–Richards treatment of exchange-induced relaxation. Despite observing a diamagnetic system, R2,eff is dominated by large Larmor frequency jumps and thus allows detection of otherwise inaccessible analyte concentrations with a single spin echo train (only 0.01% of the overall hyperpolarized spins need to be transiently bound to the molecule). The two Xe hosts cryptophane-A monoacid (CrA-ma) and cucurbit[6]uril (CB6) represent two exemplary families of container molecules (the latter one also serving as drug delivery vehicles) that act as highly efficient phase shifters for which we observed unprecedented exchange-induced relaxivity r2 (up to 866 s−1 mM−1). By including methods of spatial encoding, multiple data points can be collected simultaneously to isolate the exchange contribution and determine the effective exchange rate in partially occupied binding sites with a single delivery of hyperpolarized nuclei. The relaxivity is directly related to the guest turnover in these systems and temperature-dependent measurements yield an activation energy of EA = 41 kJ mol−1 for Xe@CrA-ma from simple relaxometry analysis. The concept is transferable to many applications where Xe is known to exhibit large chemical shifts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...