Discrete Helmholtz model: a single layer of correlated counter-ions. Metal oxides and silica interfaces, ion-exchange and biological membranes
Abstract
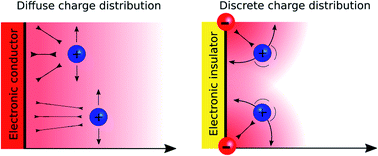
The mechanism by which interfaces in solution can be polarised depends on the nature of the charge carriers. In the case of a conductor, the charge carriers are electrons and the polarisation is homogeneous in the plane of the electrode. In the case of an insulator covered by ionic moieties, the polarisation is inhomogeneous and discrete in the plane of the interface. Despite these fundamental differences, these systems are usually treated in the same theoretical framework that relies on the Poisson–Boltzmann equation for the solution side. In this perspective, we show that interfaces polarised by discrete charge distributions are rather ubiquitous and that their associated potential drop significantly differs from those of conductor–electrolyte interfaces. We show that these configurations, spanning liquid–liquid interfaces, charged silica–water interfaces, metal oxide interfaces, supercapacitors, ion-exchange membranes and even biological membranes can be uniformly treated under a common “Discrete Helmholtz” model where the discrete charges are compensated by a single layer of correlated counter-ions, thereby generating a sharp potential drop at the interface.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...