Exploring modular reengineering strategies to redesign the teicoplanin non-ribosomal peptide synthetase†
Abstract
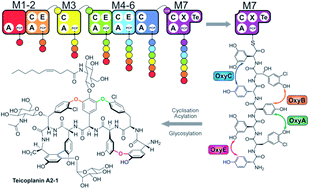
Non-ribosomal peptide synthesis is an important biosynthesis pathway in secondary metabolism. In this study we have investigated modularisation and redesign strategies for the glycopeptide antibiotic teicoplanin. Using the relocation or exchange of domains within the NRPS modules, we have identified how to initiate peptide biosynthesis and explored the requirements for the functional reengineering of both the condensation/adenylation domain and epimerisation/condensation domain interfaces. We have also demonstrated strategies that ensure communication between isolated NRPS modules, leading to new peptide assembly pathways. This provides important insights into NRPS reengineering of glycopeptide antibiotic biosynthesis and has broad implications for the redesign of other NRPS systems.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2020 Chemical Science HOT Article Collection


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...