Temperature-modulated selective C(sp3)–H or C(sp2)–H arylation through palladium catalysis†
Abstract
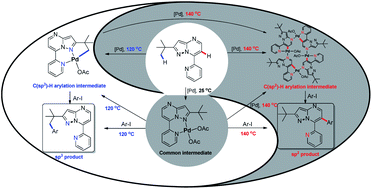
Transition metal-catalysed C–H bond functionalisations have been extensively developed in organic and medicinal chemistry. Among these catalytic approaches, the selective activation of C(sp3)–H and C(sp2)–H bonds is particularly appealing for its remarkable synthetic versatility, yet it remains highly challenging. Herein, we demonstrate the first example of temperature-dependent selective C–H functionalisation of unactivated C(sp3)–H or C(sp2)–H bonds at remote positions through palladium catalysis using 7-pyridyl-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine as a new directing group. At 120 °C, C(sp3)–H arylation was triggered by the chelation of a rare [6,5]-fused palladacycle, whereas at 140 °C, C(sp2)–H arylation proceeded instead through the formation of a 16-membered tetramer containing four 7-pyridyl-pyrazolo[1,5-a]pyrimidine–palladium chelation units. The subsequent mechanistic study revealed that both C–H activations shared a common 6-membered palladacycle intermediate, which was then directly transformed to either the [6,5]-fused palladacycle for C(sp3)–H activation at 120 °C or the tetramer for C(sp2)–H arylation at 140 °C with catalytic amounts of Pd(OAc)2 and AcOH. Raising the temperature from 120 °C to 140 °C can also convert the [6,5]-fused palladacycle to the tetramer with the above-mentioned catalysts, hence completing the C(sp2)–H arylation ultimately.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...