Mechanistic details of the cobalt-mediated dehydrogenative dimerization of aminoquinoline-directed benzamides†
Abstract
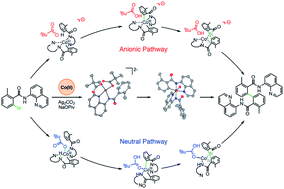
Key mechanistic features of the cobalt-mediated and aminoquinoline-directed dehydrogenative aryl–aryl coupling were investigated computationally and experimentally. A series of CoII and CoIII complexes relevant to the proposed reaction cycle have been synthesized and characterized. Stoichiometric reactions and electrochemical studies were used to probe the role of different additives in the reaction pathway. Computationally, three different mechanisms, such as charge neutral, anionic, and dimetallic were explored. It is shown that the mono-metallic anionic and charge neutral mechanisms are the most favorable ones, among which the former mechanism is slightly more encouraging and proceeds via the: (a) concerted-metalation-deprotonation (CMD) of the first benzamide C–H bond, (b) PivOH-to-PivO− rearrangement, (c) CMD of the second benzamide C–H bond, (d) C–C coupling, (e) product formation facilitated by the amide nitrogen re-protonation, and (f) catalyst regeneration. The rate-determining step of this multi-step process is the C–C coupling step. The computational studies suggest that the electronics of both the aryl-benzamide and pyridine fragments of the aminoquinoline-benzamide ligand control the efficiency of the reaction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...