A magnetic solder for assembling bulk covalent adaptable network blocks†
Abstract
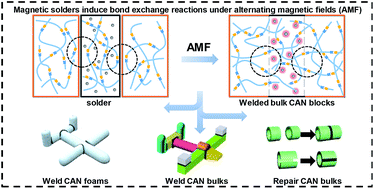
Covalent adaptable networks (CANs) represent a novel covalently cross-linked polymer that is capable of being reprocessed and recycled relying on reversible covalent bond structures and present exceptional opportunities in a wide range of prospective applications. However, it is genuinely difficult to fabricate bulk CAN blocks with solid-core geometries that possess complex shapes or multiple materials, which are crucial in cutting-edge fields such as soft robotics, flexible electronic devices and biomedical engineering. Here we report a welding technique to strategically construct complex and heterogeneous 3D CAN structures by utilizing a solder doped with magnetic nanoparticles. The solder is able to induce a bond exchange reaction at the interface between the to-be-welded pieces. Using this method, not only CAN bulks with the same materials can be welded to form complex geometries, distinctive bulks with different physical properties and chemical compositions can also be connected to fabricate multimaterial devices. Besides, this method can be used to repair damaged CAN materials and efficiently recycle scrap CAN materials, which can effectively save resources and protect the environment. The universality and robustness of this strategy is expected to promote CAN application in broader functional polymer fields.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Celebrating 10 years of Chemical Science


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...