First-generation species-selective chemical probes for fluorescence imaging of human senescence-associated β-galactosidase†
Abstract
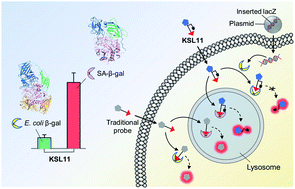
Human senescence-associated β-galactosidase (SA-β-gal), the most widely used biomarker of aging, is a valuable tool for assessing the extent of cell ‘healthy aging’ and potentially predicting the health life span of an individual. Human SA-β-gal is an endogenous lysosomal enzyme expressed from GLB1, the catalytic domain of which is very different from that of E. coli β-gal, a bacterial enzyme encoded by lacZ. However, existing chemical probes for this marker still lack the ability to distinguish human SA-β-gal from β-gal of other species, such as bacterial β-gal, which can yield false positive signals. Here, we show a molecular design strategy to construct fluorescent probes with the above ability with the aid of structure-based steric hindrance adjustment catering to different enzyme pockets. The resulting probes normally work as traditional SA-β-gal probes, but they are unique in their powerful ability to distinguish human SA-β-gal from E. coli β-gal, thus achieving species-selective visualization of human SA-β-gal for the first time. NIR-emitting fluorescent probe KSL11 as their representative further displays excellent species-selective recognition performance in biological systems, which has been herein verified by testing in senescent cells, in lacZ-transfected cells and in E. coli-β-gal-contaminated tissue sections of mice. Because of our probes, it was also discovered that SA-β-gal content in mice increased gradually with age and SA-β-gal accumulated most in the kidneys among the main organs of naturally aging mice, suggesting that the kidneys are the organs with the most severe aging during natural aging.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...