Influence of the physicochemical features of TiO2 nanoparticles on the formation of a protein corona and impact on cytotoxicity†
Abstract
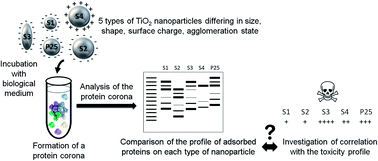
Due to their unique properties TiO2 nanoparticles are widely used. The adverse effects they may elicit are usually studied in relation to their physicochemical features. However, a factor is often neglected: the influence of the protein corona formed around nanoparticles upon contact with biological media. Indeed, although it is acknowledged that it can strongly influence nanoparticle toxicity, it is not systematically considered. The aim of this study was to characterize the formation of the protein corona of TiO2 nanoparticles as a function of the main nanoparticle properties and investigate potential relationship with the cytotoxicity nanoparticles induce in vitro in human lung cells. To that purpose, five TiO2 nanoparticles differing in size, shape, agglomeration state and surface charge were incubated in cell culture media (DMEM or RPMI supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum) and the amount and profile of adsorbed proteins on each type of nanoparticle were compared to their toxicological profile. While nanoparticle size and surface charge were found to be determinant factors for protein corona formation, no clear impact of the shape and agglomeration state was observed. Furthermore, no clear relationship was evidenced between the protein corona of the nanoparticles and the adverse effect they elicited.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...